Silicon carbide (SiC) is an ideal material for manufacturing focus rings, because the focus rings will be in direct contact with the plasma in the vacuum reaction chamber, so a material that can resist plasma corrosion is required. Traditionally, focus rings are made of silicon or quartz, but these materials have poor etching resistance in fluorine-containing plasmas, resulting in severe corrosion of equipment components after a period of use, thereby reducing production efficiency.
Silicon carbide focus rings are superior to traditional silicon-based focus rings in many aspects, including:
1. High density, which can reduce the amount of etching;
2. Higher band gap, providing excellent insulation performance;
3. High thermal conductivity and low expansion coefficient, so that it can withstand thermal shock;
4. High elasticity, so that it has good resistance to mechanical shock;
5. High hardness, making it wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant.
The electrical conductivity of silicon carbide is similar to that of silicon, and it has good resistance to ion etching. With the advancement of integrated circuit miniaturization, the demand and importance of etching processes are increasing, especially in capacitively coupled (CCP) plasma etching equipment, where the required plasma energy is higher, so the use rate of focus rings made of silicon carbide materials is increasing.
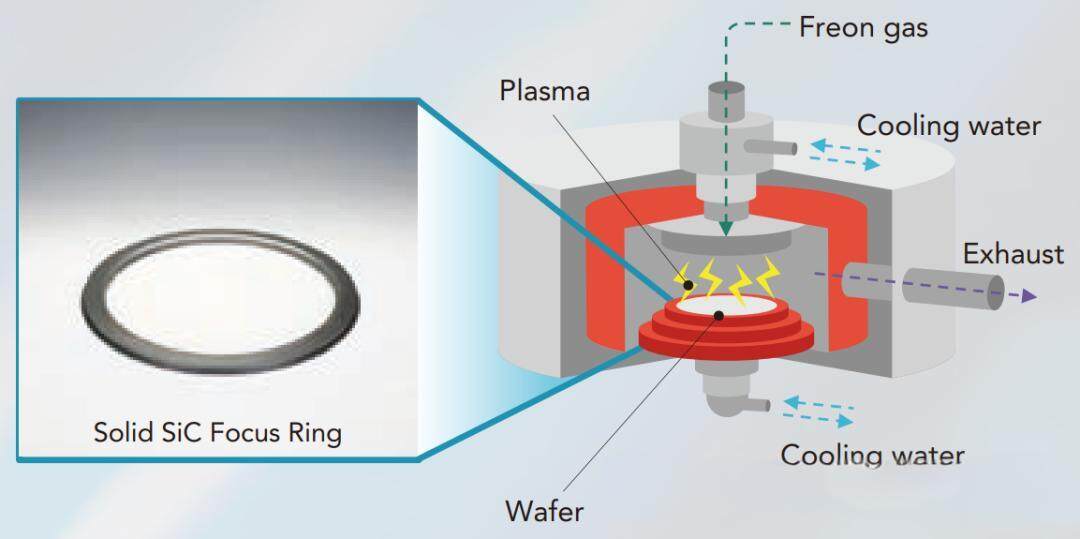
In the field of silicon carbide parts for semiconductor equipment, companies in the industry generally use chemical vapor deposition (CVD) for production. The focus ring is a process in which silicon carbide generated by chemical reactions is deposited into a certain shape by vapor deposition, and then the silicon carbide in a certain shape is machined to generate the focus ring according to specific conditions of use. In this process, the ratio of raw materials involved in vapor deposition is fixed after many experiments, so the properties of the silicon carbide focus ring produced, such as resistivity, are also fixed. However, for plasma etching equipment, fixed resistivity is not always applicable to different etching equipment. When a focus ring with lower resistivity or a focus ring with higher resistivity is required, since the ratio of raw materials involved in vapor deposition needs to be changed, it is necessary to re-experiment and re-determine the ratio of raw materials. This process is long and costly.
In summary, silicon carbide is an ideal material for focusing rings due to its excellent performance, but there are certain challenges in adjusting parameters such as resistivity during its manufacturing process. Experiments are needed to optimize the raw material ratio to meet the needs of different equipment.
